Crystallizer Design Considerations
Crystallizer Design Considerations:
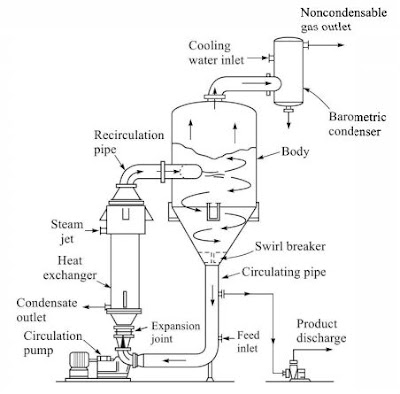 |
| Figure 1. Forced circulation evaporative crystallizer. |
The function of a crystallizer is to produce crystals of a given size specification from a feed are a specific rate. A suitable and adequate supersaturation is created by cooling the feed or by partial evaporation of the solvent. The second method is more common in industrial practice. It has been mentioned before that a narrow particle size distribution of the product is desired to maintain a good product quality. Besides the correct supersaturation and environment (i.e. agitation, pumping rate etc.), techniques like redissolution or classified product removal are helpful to achieve a better product quality. Bath crystallizers require seeding (i.e. addition of fine crystals that act as nuclei). Secondly, nucleation occurs continuously in a continuous crystallizer and seeding is not generally necessary.
The more important parameters and quantities involved in the design of a crystallizer are stated below.
The Feed Rate And State (concentration, temperature pressure, etc.):
These are specified in the design problem.The Desired Crystal Size Distribution (CSD) And Yield:
These are also generally given. The percentage theoretical yield is defined as:
Where Qi = feed rate, Qo = rate of outflow of mother liquor, Cin = feed concentration, and Cs = solubility of the solid at the exit temperature. In the expression for ‘theoretical yield’, the exit liquid is assumed to have lost the supersaturation. If the temperature in the crystallizer is fixed, Cs can be obtained from the solubility data. From the specified yield (%), Qo is calculated using the above equation. The required rate of evaporation is determined by a solvent balance.
Solvent Evaporation Rate And The Heat Transfer Area Required:
These are to be calculated. The evaporation rate is calculated from material balance. A heat balance over the crystallizer gives the required rate of heat input. The heat of crystallization should be included in the heat balance. The steam or the heating fluid rate and the heat transfer area are then calculated.
Crystallizer Volume:
This is to be calculated. For this purpose, experimental data on nucleation and the growth rate (G) are required. These data can be obtained from a laboratory crystallizer. Data collected from a pilot plant crystallizer of volume around 50 liters or more can be more reliably used. If the product quality (in terms of the weight % of the crystals above particular size) is specified in the design problem, the equation given below may be solved for the dimensionless cut-off size, x.
From the known values of growth rate (G) and crystal size (L), the holdup time and volume can be calculated. The diameter of a crystallizer is frequently determined on the basis of possible entrainment of liquid with the vapor generated.
Crystallizer Dimension And Recirculation Rate:
These are to be calculated and checked. The recirculation rate of the slurry through the heat exchanger (see Figure 1) is important in the heat transfer area calculation. The selected crystallizer diameter and recirculation rate should be checked so that adequate velocity is maintained to avoid settling of solid depending upon the type of crystallizer.
Reference:
- Binay K. Dutta, Principles of Mass Transfer and Separation Processes. Chapter 13 (2009).
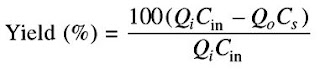



hi
ReplyDeleteThanks For Shareing This you blog is Really very nice in this blog I relly like this topic.Furnaces utilize a heat exchanger to transport warm air throughout your house. It is a critical component of your heating system. Any problems with It will not only cause your furnace to break down. But it will also endanger the health and safety of your family.
ReplyDeleteThank you for the helpful blog, "Crystallizer Design Considerations." I want you to know that your information is invaluable for aspiring candidates. Keep sharing valuable updates!
ReplyDeleteChandu Biology Classes